Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease that continues to be a major global health concern. With its diverse range of forms and the impact it has on individuals and families, understanding cancer is essential for raising awareness and promoting prevention and early detection efforts. In this article, we delve into the causes, types, and prevention strategies for this disease.
Causes of Cancer: Unraveling the Complexity
Cancer arises from the uncontrolled growth and division of cells within the body. While the exact cause of cancer can be attributed to various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental influences play a significant role. Carcinogens, which are substances capable of causing cancer, can be found in pollutants, tobacco smoke, and even certain foods. Furthermore, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, ionizing radiation, and certain chemicals can also increase the risk of cancer development.
Types of Cancer: A Wide Spectrum of Variants
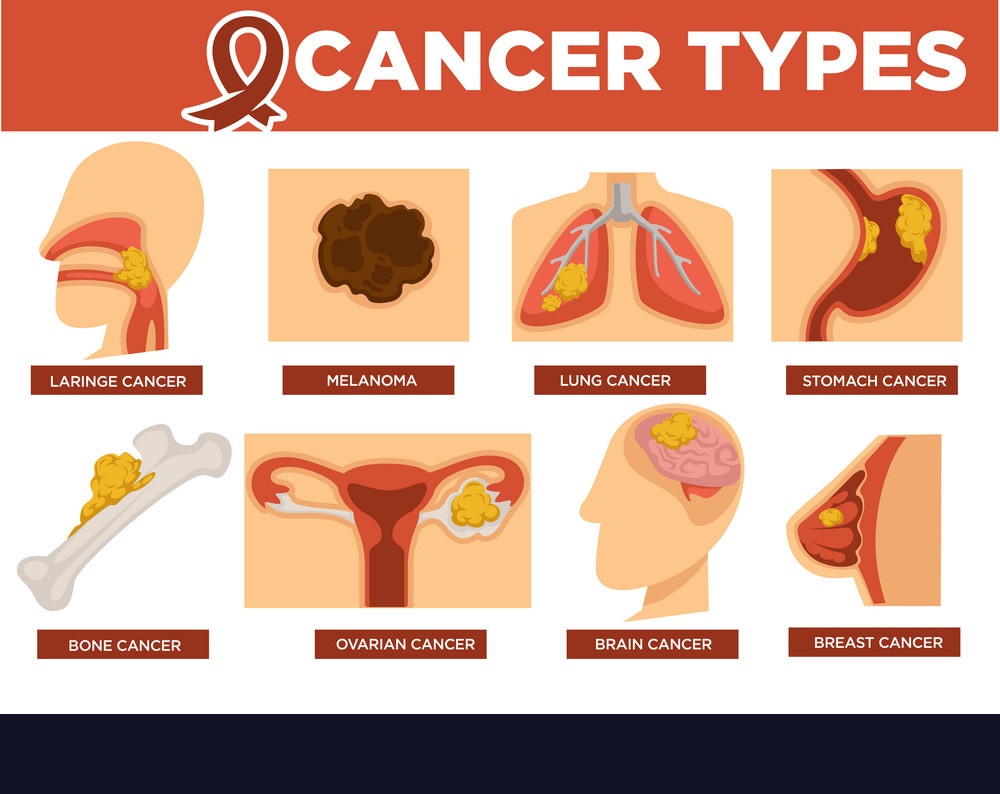
Cancer isn’t a singular disease but rather a collection of diseases that can affect virtually any part of the body. Common types of cancer include breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, and skin cancer. Each type has its own distinct characteristics, risk factors, and treatment approaches. Early detection through regular screenings and understanding the symptoms associated with each type can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment.
Prevention Strategies: Empowering Individuals
Preventing cancer involves adopting a proactive approach to reduce risk factors and promote healthy lifestyles. Here are some key strategies that can contribute to cancer prevention:
Healthy Diet:
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support the body’s defense mechanisms against cancer.
physical activity:
Regular exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also reduces the risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast and colon cancer.
Tobacco Avoidance:
Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke is one of the most effective ways to prevent various types of cancer.
Sun Protection:
Limiting exposure to UV radiation by using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding tanning beds can help prevent skin cancer.
Vaccinations:
Some viruses, such as HPV and hepatitis B, are linked to an increased risk of cancer. Vaccinations against these viruses can significantly reduce the likelihood of cancer development.
The Power of Early Detection
Early detection plays a crucial role in successful cancer treatment. Regular screenings, self-examinations, and awareness of potential warning signs are essential. Common early warning signs include persistent changes in bowel or bladder habits, unexplained weight loss, unusual bleeding or discharge, and persistent cough or hoarseness.
.
Causes of Cancer: Unraveling the Complexity
Cancer development is a result of mutations or changes in the DNA of cells. Mutations can occur due to a combination of genetic predisposition and exposure to environmental factors. Some individuals inherit genetic mutations from their parents that increase their susceptibility to cancer. For instance, certain mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are associated with a higher risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
Exposure to carcinogens can trigger DNA mutations. These carcinogens can be found in substances like tobacco smoke, asbestos, benzene, and formaldehyde. The body has natural defense mechanisms that repair damaged DNA, but when these mechanisms fail, cells can begin to divide uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors.
Types of Cancer: A Wide Spectrum of Variants
Cancers are classified based on the type of tissue they originate from. Carcinomas are cancers that start in the epithelial cells that cover the body’s internal and external surfaces. Sarcomas begin in the connective tissues, such as bones, muscles, and cartilage. Leukemias start in blood-forming tissues like the bone marrow, while lymphomas develop in the lymphatic system.
Each type of cancer has distinct risk factors and characteristics. For example, breast cancer is more common in women, especially those with a family history of the disease. Lung cancer is closely linked to tobacco smoking, and early detection is challenging due to its often asymptomatic nature in the early stages. Prostate cancer is predominantly found in males and typically grows slowly.
Prevention Strategies: Empowering Individuals
Apart from the strategies mentioned earlier, maintaining a healthy body weight is crucial in cancer prevention. Obesity is associated with an increased risk of various types of cancer, including breast, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding excessive sun exposure are also important steps in reducing cancer risk.
Regular health check-ups and cancer screenings are invaluable tools for early detection. Mammograms, Pap smears, colonoscopies, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests are some of the screenings that can detect cancer at an early stage when treatment is most effective.
The Power of Early Detection
Early detection allows for more treatment options and a higher chance of successful outcomes. The stages of cancer are generally classified as Stage 0 to Stage IV, with Stage 0 indicating cancer in situ (localized) and Stage IV indicating cancer that has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic). Survival rates are typically higher for cancers detected in earlier stages, highlighting the importance of screenings and self-examinations.
Advancements in Cancer Treatment: Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy
Cancer treatment has come a long way, with advancements that offer more personalized and effective approaches. Targeted therapies focus on specific molecular changes in cancer cells that drive their growth. These therapies aim to block the signals that promote tumor growth while minimizing damage to healthy cells. Immunotherapy, on the other hand, harnesses the body’s own immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. This approach has shown promising results in various types of cancer, including melanoma, lung cancer, and certain types of leukemia.
Support for Cancer Patients: Holistic Care
Cancer not only affects the body physically but also takes a toll on emotional and mental well-being. Supportive care services are crucial for patients and their families to navigate the challenges that come with a cancer diagnosis. Psychosocial support, counseling, and patient education help individuals cope with the emotional impact of cancer and its treatments. Additionally, complementary therapies like yoga, meditation, and art therapy can contribute to a holistic approach to healing.
Research and Breakthroughs: Looking Towards the Future
Ongoing research is essential to uncover new insights into cancer biology, risk factors, and treatment options. Scientists are continually discovering genetic mutations associated with specific cancers, enabling more targeted interventions. Breakthroughs in genomics have paved the way for precision medicine, where treatments are tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup. Clinical trials also play a critical role in testing innovative therapies and advancing the field of oncology.
Global Impact and Collaborative Efforts
Cancer knows no boundaries, affecting individuals across the globe. International organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Cancer Society (ACS), work together to provide resources, raise awareness, and promote cancer prevention and control. Collaborative efforts between governments, healthcare organizations, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are essential in tackling cancer’s global impact.
Cancer Advocacy: Raising Awareness and Empowering Change
Advocacy plays a vital role in the fight against cancer. Awareness campaigns, fundraising events, and support groups contribute to educating the public and generating resources for research and patient support. Cancer survivors and their families often become advocates, sharing their stories to inspire others and call for policy changes that improve cancer care and access to treatment.
Conclusion:
Hope on the Horizon
While the challenges posed by cancer are formidable, there is a sense of hope and determination that pervades the field of oncology. Through continued research, early detection efforts, innovative treatments, and global collaboration, we are making strides towards reducing the impact of cancer on individuals and society. By fostering a comprehensive approach that encompasses prevention, treatment, and support, we can create a world where cancer is not only understood but also managed effectively.
A Collective Effort
Advancements in cancer research and treatment have led to improved survival rates and quality of life for many individuals diagnosed with cancer. However, there is still much work to be done. Continued research, education, and awareness campaigns are essential in the fight against cancer. By uniting efforts on a global scale, we can work towards reducing the incidence of cancer, improving early detection, and enhancing treatment options.As our understanding of cancer evolves, so do our strategies for prevention and treatment. The battle against cancer requires a collaborative effort involving healthcare professionals, researchers, policymakers, and individuals. By staying informed about risk factors, adopting healthy lifestyle choices, and promoting awareness, we can collectively work towards a world where the burden of cancer is significantly reduced.